From Advances in
New Crops, Proceedings of the First National Symposium NEW
CROPS: Research, Development, Economics
by Christiane Cabral Velho, Anna Whipkey, and Jules Janick
Cupuassu: A New Beverage Crop for Brazil
1. INTRODUCTION
2. BOTANY
1. Origin
2. Morphology
3. HORTICULTURE
1. Culture
2. Tissue Culture
4. UTILIZATION
5. FUTURE PROSPECTS
6. REFERENCES
7. Table 1
8. Table 2
9. Fig. 1
10. Fig. 2
11. Fig. 3
12. Fig. 4
13. Fig. 5
INTRODUCTION
Brazil
is the largest producer of tropical and subtropical fruits in the
southern hemisphere. Exports of orange and banana have shown marked
increase over the last decade. Currently Brazil is searching for ways
to diversify its export industry and exploit indigenous species of the
tropical rainforest (Chaar 1980, Venturieri et al. 1985).
A promising new fruit is cupuassu [Theobroma grandiflorum (Willd ex Spreng) Schum, Sterculiaceae], a close relative of cacao (T. cacao
L.). Cupuassu fruit contains a highly-flavored pulp that can be used
for juices, ice creams, liquors, wine, and jellies (Vasconcelos et al.
1975). The seeds can be used to make chocolate (Vasconcelos et al.
1975, Venturieri and Martel 1985). The volume processed by local
industries in Para region has increased, although fruits are still
harvested from wild trees (Calzavara et al. 1984).
BOTANY
Origin
Cupuassu
originated in south and southeastern Amazonia in Brazil and is also
native to the states of Para and Maranhao. Today, it can be found near
the Tapajos, Xingu, and Guama rivers, and in northeastern Maranhao
(Vasconcelos et al. 1975).
Morphology
Cupuassu, is an erect tree, that can attain heights over 20 m at
maturity, but when cultivated, is maintained at 6 to 8 m. The canopy
can reach 7 m in diameter; oblong leaves are 25 to 35 cm wide. The
inflorescence has three to five flowers. Each flower has a calyx
composed of five triangular fused sepals, a corolla with five purple
petals, five purple staminodes, five stamens, and an ovary with five
locules. The oblong fruits are 12 to 25 cm long, 10 to 12 cm in
diameter, and weigh I to 2 kg. A four to five-year-old tree may produce
20 to 30 fruits and a mature tree (over seven years) 60 to 70. Each
fruit contains about 50 seed which are surrounded by a mucilaginous
pulp with an acid taste and a strong "goaty" aroma (Chaar 1980,
Venturieri and Alves 1985, Venturieri et al. 1985).
Cupuassu is
cross-pollinated, with bees the main pollinator (Falcao and Lleras
1983). The rate of pod set is low because of the high incidence of
flower bud abortion. Anther dehiscence precedes anthesis which occurs
between 10:00 am and 5:30 pm. Flower bud development takes 15 days and
fruits mature four months after fertilization (Silva Retto, 1986).
Calzavara et al. (1984) has classified cupuassu by fruit shape:
Redondo: the apex of the fruit is rounded; the most common type (Fig. 1, Fig. 2 right, Fig. 3 right).
Mamorana: the fruit has a pointed apex and a very thick rind (7 to 9 mm).
Mamau: a seedless clone found in Para (EMBRAPA/CPATU) (Fig. 2 left, Fig. 3 left).
The
seeded cupuassu fruit consists of 46% pulp, 38% rind, and 16% seeds.
The seedless fruit consists of 67% pulp, but the pulp is somewhat less
flavorful. Another problem with the seedless clone is low productivity
(Chaar 1980). The constituents of cupuassu pulp are listed in
Table 1.
HORTICULTURE
Culture
Cupuassu
can be cultivated in the humid tropics with an average annual rainfall
of 1,800 mm and an annual mean temperature of 23°C. Cupuassu grows well
in deep soils with high fertility. Germination of cupuassu is inhibited
by the mucilage which surrounds the seeds. The mucilage can be removed
by light fermentation for 12 to 24 hours; germination starts three to
four days later. Seeds are then sown directly in plastic bags or trays.
If the mucilage is not removed, germination takes 12 to 17 days
(Venturieri and Alves 1985, Venturieri et al. 1985).
Young
seedlings are protected by 50% shading of direct sun. When the
seedlings are five to six months old, light is increased to 75% of full
sun. For rootstock production, seedlings four to six months old are
used. Recommended propagation methods are side grafting or green strip
budding (Calzavara et al. 1984, Venturieri et al. 1985, Venturieri et
al. 1986/1987). Plants are spaced 5 m apart with successive pruning
until the seventh or eighth year. The fertilizer used is the same as
for cacao (12-5-10 NPK) plus manure.
The most common insect
pests are Coleoptera, aphids, bees, and several species of
Crysomelidae. The most common diseases are witches broom incited by Crinipellis perniciosa, anthracnose (Colletotrichum gloesporioides) and "queima do fio" (Pellicularia koleroga) (Venturieri et al. 1985).
Tissue Culture
Somatic
embryogenesis has been induced in cupuassu by culturing immature
zygotic embryos on a semisolid Murashige and Skoog medium supplemented
with 1 mg/liter 2,4-D and 10% coconut water (Janick and Whipkey 1988).
Somatic embryos proliferate by budding and produce embryogenic
competent callus (Fig. 4). Once induced, embryogenic cultures were most
proliferative on 2,4-D-free medium and glucose. Somatic embryos have
not produced viable seedlings.
UTILIZATION
The
fruit has various uses as shown in Fig. 5 (Calzavara et al. 1984). The
value of the seed of cupuassu is still not widely recognized and they
are usually discarded. The fatty acid composition of cupuassu and cacao
seed is shown in Table 2 (Calzavara et al. 1984, Chaar 1980,
Vasconcelos et al. 1975). On the basis of the high linoleic acid
content, the seed "butter" of cupuassu would be expected to have a
lower melting point than cocoa butter. The use of cupuassu seeds for
chocolate manufacture is restricted to the Solimoes, Madeira, and
Tocantins rivers valleys of the Amazon.
Currently, cupuassu pulp
can be extracted directly, frozen or processed as a syrup, with water
and sugar (Chaar 1980). Pulp extraction is performed manually or
mechanically. During manual extraction, the pulp is cut with a scissors
and seeds are removed by hand. In the mechanical process, the pulp is
extracted by a depulping machine, then homogenized and pasteurized.
Machines have been developed that can process up to 2,500 kg of fruit
per hour (Calzavara et al. 1984). The pulp must be frozen because the
flavor is destroyed by heat.
FUTURE PROSPECTS
Cupuassu
because of its unusual aroma may have real promise as a new flavor for
many products, particularly ice-creams, yogurts, and tropical juices.
However, there are a number of agricultural problems that must be
overcome including high susceptibility to witches broom and short
storage life of the fruit. Immediate processing by freezing is required
because heat destroys flavor. Cupuassu has the potential to become a
new crop for the tropical rainforest providing research continues in
culture, selection, processing, and marketing. Investigations are
presently underway in the Instituto Nacional de Pesquisa da Amazonia
(INPA), and Centro de Pesquisa Agropecuaria do Tropico Umido
(CPATU/EMBRAPA).
REFERENCES
Calzavara,
B.B.G., C.H. Muller, and O. Kabwage. 1984. Fruticultura tropical: o
cupuacuzeiro. Belem, EMBRAPA/CPATU. Documentos 32.
Chaar, J.M. 1980. Composicao do cupuacu [Theobroma grandiflorum (Schum)] e conservacao do seu nectar por meios fisicos e quimicos. MS Thesis, UFRRJ, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
Falcao, M.A. and E. Lleras. 1983. Aspectos fenologicos, ecologicos e de produtividade do cupuacu. Theobroma grandiflorum (Willd ex Spreng) Schum. Acta Amazonica 13:725-735.
Janick, J. and A. Whipkey 1988. Somatic embryogenesis in Theobroma grandiflorum. HortScience 23:807. (Abstr.)
Silva Retto. A. 1986. Estudos preliminares sobre a biologia floral do cupuacuzeiro [Theobroma grandiflorum (Willd ex Spreng) Schum]. BS Thesis, FUA, Manaus, Brazil.
Vasconcelos,
M.N.Z., M. Leao da Silva, J.G. Soares Maia, and O.R. Gottlieb. 1975.
Estudos quimicos das sementes do cupuacu. Acta Amazonica 5:293-295.
Venturieri, G.A. and J.P.L. Aguiar. 1986. Composicao do chocolate caseiro de amendoas de cupuacu [Theobroma grandiflorum (Willd ex Spreng) Schum]. INPA, Manaus, Brazil.
Venturieri, G.A. and M.LB. Alves. 1985. A culture do cupuacuzeiro. CEAGRO/GEDEI, Rondonia, Brazil.
Venturieri, G.A., M.L.B. Alves, and M.D. Nogueira. 1985. O cultivo do cupuacuzeiro. Infor. Soc. Bras. Fruticultura 4:15-17.
Venturieri, G.A. and J.H.I. Martel. 1985. Coleta de germoplasma de cupuacu [Theobroma grandiflorum (Willd ex Spreng) Schum] na pre-amazonia maranhense. INPA, Manaus, Brazil.
Venturieri, G.A., J.H.I. Martel, and G.M.E. Machado. 1986/1987. Enxertia do cupuacuzeiro [Theobroma grandiflorum (Willd ex Spreng) Schum] com o uso de gemas e garfos com e sem toalete. Acta Amazonica 16/17:27-40.
Table 1. Analysis of cupuassu pulp (Chaar 1980).
| Constituent | Quantity | | Total soluble solids (°Brix) | 10.51 | | Titratable acidity (g citric acid anhydride % w/w) | 2.35 | | Brix/acid ratio | 4.47 | | pH | 3.60 | | Reducing sugars | 3.00 | | Nonreducing sugars | 5.81 | | Vitamin C (mg/100 g) | 28.32 | | Starch (%) | 0.96 | | Pectins (mg/100 g) | 703 | | Viscosity (cps at 21°C, 100 rpm) | 6750 | | Calcium (mg/100 g) | 3.10 | | Magnesium (mg/100 g) | 9.31 | | Total iron (mg/100 g) | 1.52 |
Table 2. Fatty acid composition as a percent of total fats in cupuassu and cacao.
| Fatty acid composition | | Fatty acid | Cupuassu | Cacao | | % of lipids | | Palmitic (C16:0) | 5.8 | 32.8 | | Stearic (C18:0) | 38.3 | 35.5 | | Oleic (C18:1) | 42.8 | 29.6 | | Aracadic (C20:0) | 4.8 | 1.0 | | Linoleic (C18:3) | 83 | 1.1 | | % of seed wt | | Total lipid | 58.0 | 57.3 |

Fig. 1. Fruit of cupuassu.
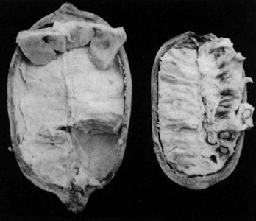
Fig. 2. Seedless (left) and seeded (right) fruit of cupuassu.
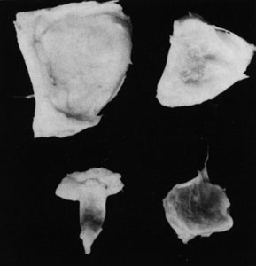
Fig. 3. Pulp segments and ovule of seedless clone (left) and seeded clone (right) of cupuassu.

Fig. 4. Somatic cotyledonary embryo of cupuassu.
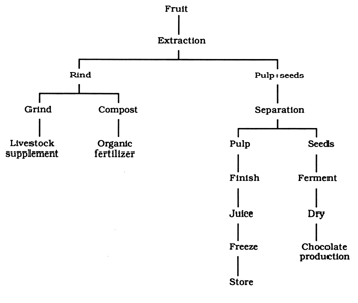
Fig. 5. Products of cupuassu fruit.
Last update August 29, 1997 by aw
|
|




